Why Startups Fail[Part 3 -Late Stage startups]
Book describes issues late stage startups face. Although get out of the early stage is difficult, this stage presents its own challenges.
Out of the frying pan
Late stage - Series C and 5 years old.
⅓ fail to earn positive returns.
Opportunity challenges
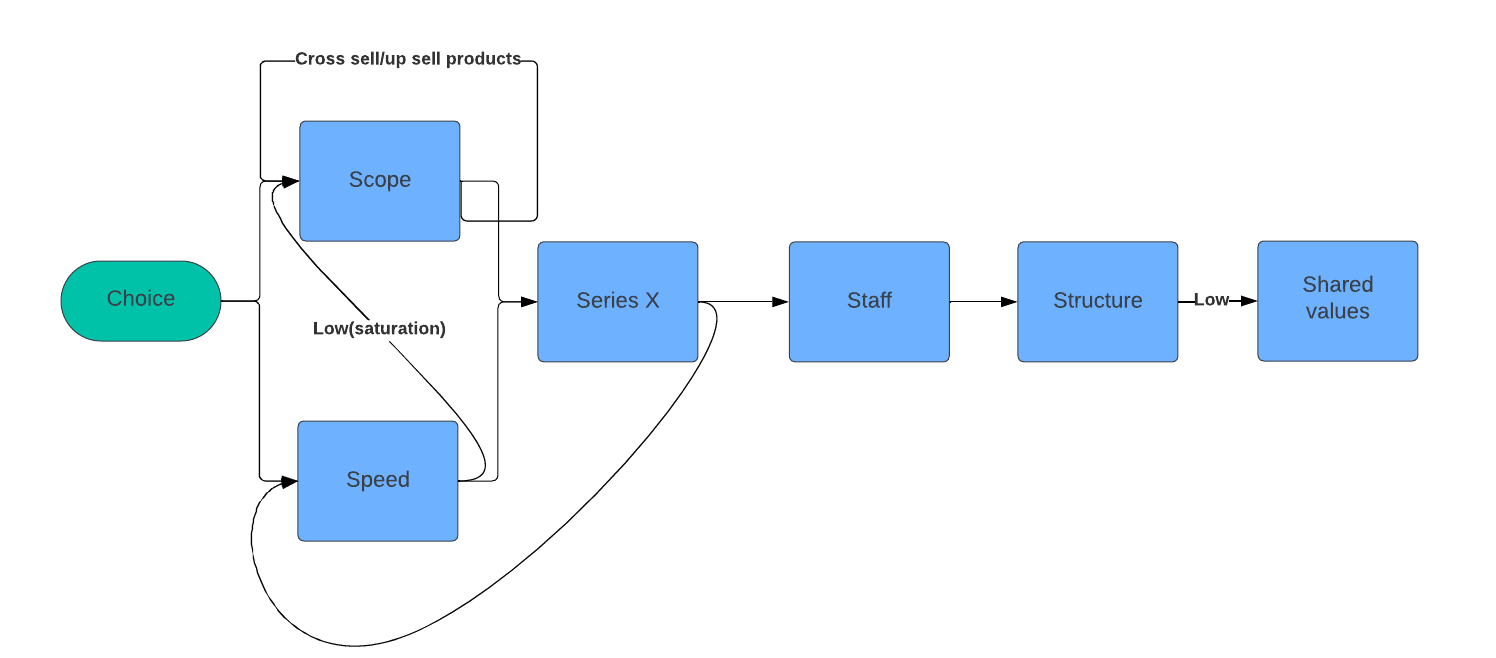
Set ambitious goals for speed and scope
Speed - pace of expansion
Scope - geographical reach, product line, innovation, vertical integration
“Goldilocks dilemma”
Resource challenges
Finance - cannot raise capital
Team
- must hire specialists on team of generalists
- Fluid management gives way to formal structures and systems
Organizational
- Distract when marketplace challenges require attention

Speed
Decide how quickly to expand core business
Scope
Geographical reach
- Costly
- Stretch management too thin
- Every market has competition, regulations & cultural differences
Product line
- Speed up development by repurposing tech
- Gain operations efficiencies by using slack capacity
Innovation
Risks:
- Raises cost of switching
- More marketing spend to educate customer
- Product development delays due to novel tech
Pros:
- ROI on new features for existing products turn negative
Vertical Integration
Risks:
- Requires investments
- Mgmt. has to acquire a new skill
Pros:
- Increases profit margins
- More consistent quality
- Mission critical functions in house
Mergers and Acquisitions
Risks:
- Overpayment
- Disappearing talent
- Integration risks - technology incompatibility, org design, cultural misfit
Pros:
- Time saving
- Cost saving after reducing redundant functions
- Avoid early stage startup risks
Series X
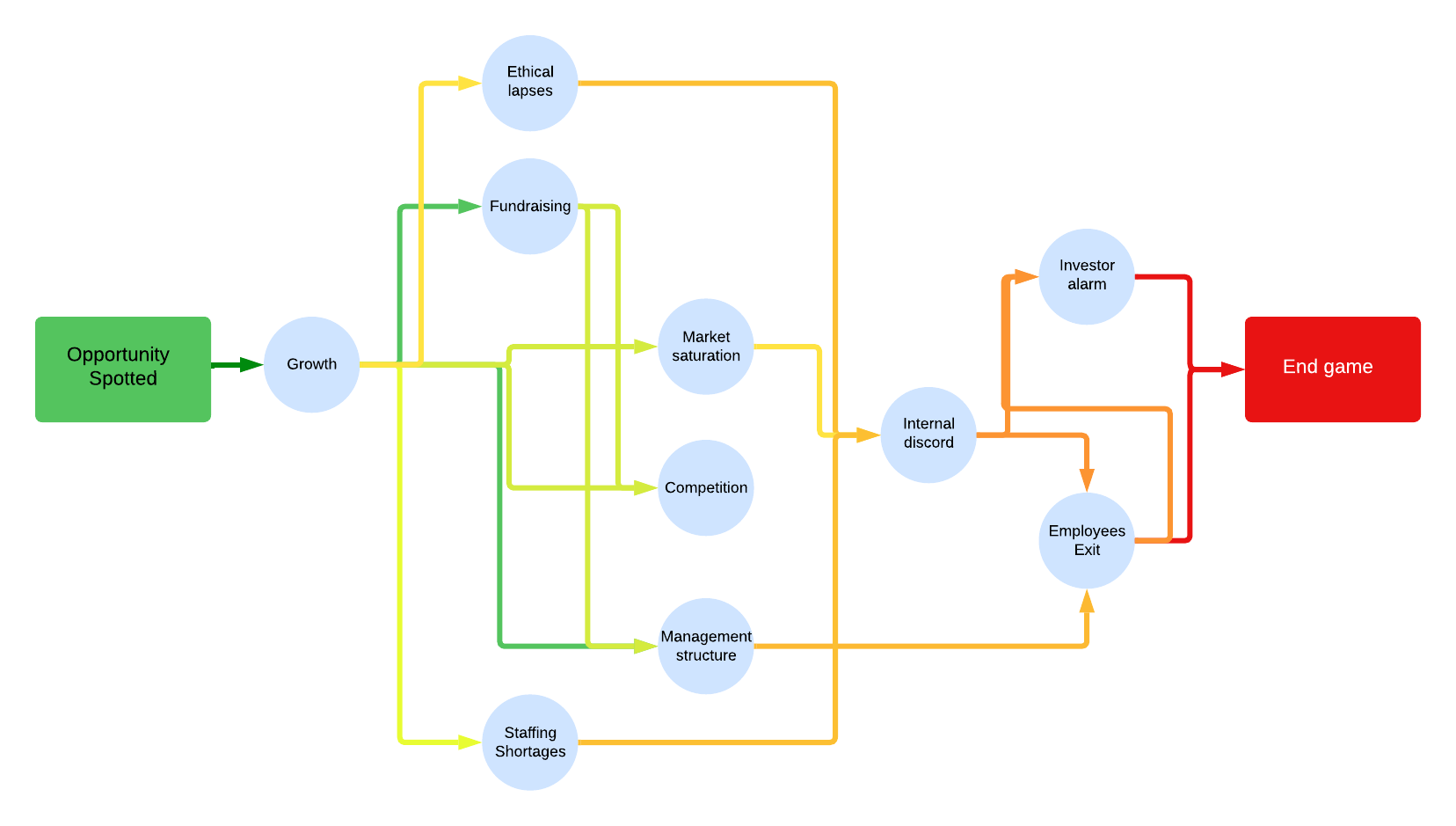
Growth pressures
Winner’s curse - VCs bid up startup value. Next round is harder to raise.
Down rounds - signals firm is struggling. Will make it difficult to attract talent.
How realistic is it to sustain momentum?
Funding risks:
- Sector falls out of favor
- Need contingency plan in case of funding drought
CEO succession - when investors > founders on board, founder loses control and ability to establish strategic priorities
Board priorities - to earn a return for late state investors, startup has to continue to remain aggressive.
Structure
Formalize org chart and introduce management systems
- Information flows to where’s it’s reduced
- Coordinate complex activities
- Cross functional conflict needs resolution
Formal org change
Additional management layer to tie break
Management structure:
- Strategic and operational planning
- Financial planning
- Performance tracking
- Employee recruitment and development
Shared Values
Employees know what to do
New employees may view employment as just a job. Lead to decay in culture. Take no initiative or be committed.
Promote culture:
- Mission and values statement
- Communicate and reinforce relentlessly
- Reinforce culture through actions
- HR practice - culture fit interview
- Measure whether employees understand mission and live up to values
Staff
Genaralists to specialists.
New CEO and management required. Skills and attitudes that makes good early stage founders is not the same as managers
"Peter pan syndrome"-long for startup's early days.
Two paths
Speed or scope
Base camps
Use quick win to:
- Refine technology
- Build early momentum
Speed trap
RAWI test
Ready - proven business model with positive profit model
Able - have human and capital resources
Willing - founders, employees and investors eager to grow
Impelled - due to rivals? Sleeping dragons? Network effects
RAW is required and founders should take test quarterly
Ready
Sustainable product market fit
LTV/CAC > 3\
Risks:
- Saturation
- Quality decrease
- Attract rivals
- Founders
- Equity dilution, get sidelines, work long hours
Use cohort tracking to mitigate saturation risk
Warning: this is lagging indicator
Increase in CAC indicates saturation.
Find indicators that are more quickly observable.
Able
Have capital, talent and leaders, structure and management systems.
Hiring issues. Avoid:
- Just hiring warm bodies
- Pressure current employees to work harder. Burn out!
- Skimp on training
Willing
Entrepreneurs has different risk-reward tradeoff than late stage investors.
Continued pressure to grow
Impelled
Network effects
Types of networks:
- Two sided
- One sided
- Cross sided
Adjusted LTV/CAC formula
LTV(1+v)/CAC > 1; v = viral coefficient
Might be worth it to seed initial customers to determine v
Switching costs
Upfront costs
- Find and vet new service
- Terminate old account
- Penalties
Disruption risk
- Changing trusted supplier not easy
Major first moved advantage
Scale economics
Reduce unit costs
- High fixed costs
- Learn by doing opportunities
- Learning curve in manufacturing
- Develop proprietary tech
Do not overinvest when:
- Cannot calculate CAC
- Hoping a greater fool will buy startup. Maybe exploiting a funding bubble
- Overconfidence and wishfull thinking
De-escalate competition when:
- Small # of players
- History of interaction
- Expect to continue to interact
- Shrared beliefs about market opportunity
- Transparent moves
- Short lag between decision and observable moves
Help wanted
Capital
Venture capital funding is prone to boom and bust cycle which effects late state ventures more since they require more capital.
Hard to find new investors when existing ones won’t invest.
Mitigate financing risks:
- Be alert about cycles
- Raise money from early investors who can provide bridge financing or be able to invest in next round
- Raise more money than required
- Have low fixed cost for flexibility. Get a short term lease.
Missing managers
Specialist from big companies can fix metrics without making an overall impact by making political moves.
Startups also need leaders to initiate moves.
Lower risk- bring a junior specialist on board. Catch-22- no one there to manage or help junior specialist grow.
Senior specialists:
- Hire using network
- Build key processes and systems
Add a HR to:
- Create process for onboarding and offboarding
- Talent development
- Manager organization structure
- Preserve company culture
- Council senior executives
Missing Systems
In a startup every function requires new systems and processes.
Having the right system in place effects scalability.
Decision making process- Who can propose initiatives? Who provides input? Who makes decision?
Moonshots and Miracles
Moonshots - meet numerous complex goals or crash
Moonshot -> momentum -> sunk costs -> “escalation of commitment”
Often launched by charismatic or egomaniacal founder
Egomaniacal founder
- Takes high tech risk
- Makes high funding demands
- Relies of big asks from partners
- Assumes government support
- Thinks there is no competition
- Estimates high demand
How to estimate demand?
- Assume survey respondents overestimate purchase intent
- Do a smoke test
- Get feedback on prototype
- Do not stay in stealth mode, get actual feedback and redo estimates
Dealing with delays:
- Accept delays as part of developing a moonshot
- Add people
- Freeze functionality
- Cut corners - remove key features or ship with bugs
Harness a monomaniacal founder:
- Use zeal and charisma to mobilize resources
- Have a “reality distortion filed”
- Watch out for narcissism
- Escalation of commitment
- Lacks empathy and takes credit for other’s work
- Surrounded by yes men
Board best practices:
- Primary way VCs add value
- Have independent directors(not investors or senior managerment)
- A CEO of a previous successful startup
- Closed session
- Review CEO performance
- Review self effectiveness